Random Sampling Example Situation | In this technique, each member of the population has an equal chance of being selected as subject. Each of these random sampling techniques are explained more fully below, along with examples of each type. Simple random sampling is the randomized selection of a small segment of individuals or members from a whole population. In this sampling method, each member of the population has an exactly for example, if young participants are systematically less likely to participate in your study, your findings might not be valid due to the underrepresentation. For example, 12% of the student population are english.
Stratified random sampling divides a population into subgroups or strata, whereby the members in each of the stratum formed have similar attributes however, the proportions in the sample are not equal to the percentages in the population. Instead of collecting feedback from 326. It provides each individual or member of a population with an equal and fair probability of being chosen. A simple random sample is a randomly selected subset of a population. Simple random sampling is the randomized selection of a small segment of individuals or members from a whole population.
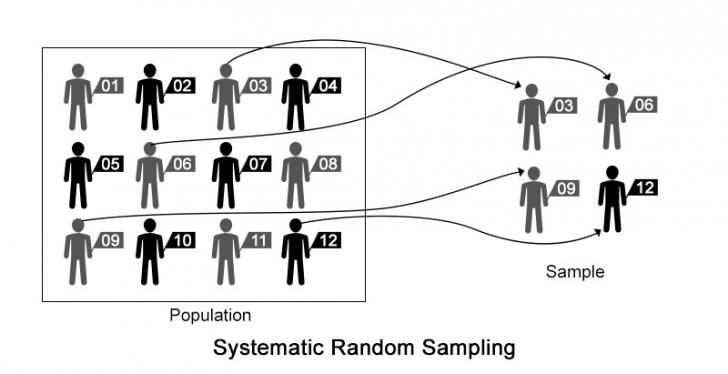
Stratified random sampling divides a population into subgroups or strata, whereby the members in each of the stratum formed have similar attributes however, the proportions in the sample are not equal to the percentages in the population. For example, 12% of the student population are english. It provides each individual or member of a population with an equal and fair probability of being chosen. One of the most obvious limitations of simple random sampling method is its need of a complete list of all the members of the population. Random sampling examples show how people can have an equal opportunity to be selected for something. Random cluster sampling would work well in a situation like this. The simple random sampling method is one of the most convenient and. Instead of collecting feedback from 326. Simple random sampling is the randomized selection of a small segment of individuals or members from a whole population. Find simple random sampling examples and other types. In this sampling method, each member of the population has an exactly for example, if young participants are systematically less likely to participate in your study, your findings might not be valid due to the underrepresentation. A simple random sample is a randomly selected subset of a population. For example, if you're selecting your samples by lottery, set aside the numbers for any members of the population you don't want to include in the drawing.
A simple random sample is a randomly selected subset of a population. For example, 12% of the student population are english. Find simple random sampling examples and other types. Random cluster sampling would work well in a situation like this. For example, if you're selecting your samples by lottery, set aside the numbers for any members of the population you don't want to include in the drawing.
Find simple random sampling examples and other types. One of the most obvious limitations of simple random sampling method is its need of a complete list of all the members of the population. Simple random sampling is the randomized selection of a small segment of individuals or members from a whole population. For example, if you're selecting your samples by lottery, set aside the numbers for any members of the population you don't want to include in the drawing. Random sampling examples show how people can have an equal opportunity to be selected for something. It provides each individual or member of a population with an equal and fair probability of being chosen. Instead of collecting feedback from 326. In this sampling method, each member of the population has an exactly for example, if young participants are systematically less likely to participate in your study, your findings might not be valid due to the underrepresentation. A simple random sample is a randomly selected subset of a population. In this technique, each member of the population has an equal chance of being selected as subject. Each of these random sampling techniques are explained more fully below, along with examples of each type. Random cluster sampling would work well in a situation like this. For example, 12% of the student population are english.
It provides each individual or member of a population with an equal and fair probability of being chosen. Instead of collecting feedback from 326. Random sampling examples show how people can have an equal opportunity to be selected for something. Stratified random sampling divides a population into subgroups or strata, whereby the members in each of the stratum formed have similar attributes however, the proportions in the sample are not equal to the percentages in the population. Random cluster sampling would work well in a situation like this.
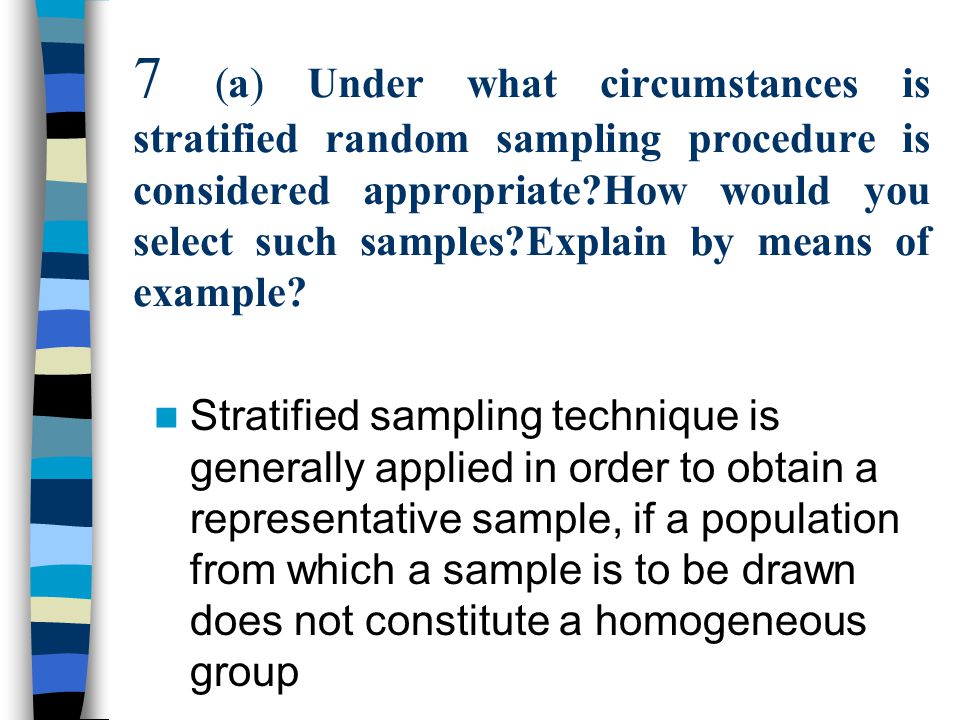
The simple random sampling method is one of the most convenient and. For example, 12% of the student population are english. Simple random sampling is the randomized selection of a small segment of individuals or members from a whole population. Random sampling examples show how people can have an equal opportunity to be selected for something. Keep in mind that cluster sampling is not as reliable as other types of random. Find simple random sampling examples and other types. Each of these random sampling techniques are explained more fully below, along with examples of each type. For example, if you're selecting your samples by lottery, set aside the numbers for any members of the population you don't want to include in the drawing. A simple random sample is a randomly selected subset of a population. One of the most obvious limitations of simple random sampling method is its need of a complete list of all the members of the population. Random cluster sampling would work well in a situation like this. In this technique, each member of the population has an equal chance of being selected as subject. In this sampling method, each member of the population has an exactly for example, if young participants are systematically less likely to participate in your study, your findings might not be valid due to the underrepresentation.
Simple random sampling is the randomized selection of a small segment of individuals or members from a whole population random sampling example. It provides each individual or member of a population with an equal and fair probability of being chosen.
Random Sampling Example Situation: In this technique, each member of the population has an equal chance of being selected as subject.
Tidak ada komentar
Posting Komentar